Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury Partial Thickness Tear
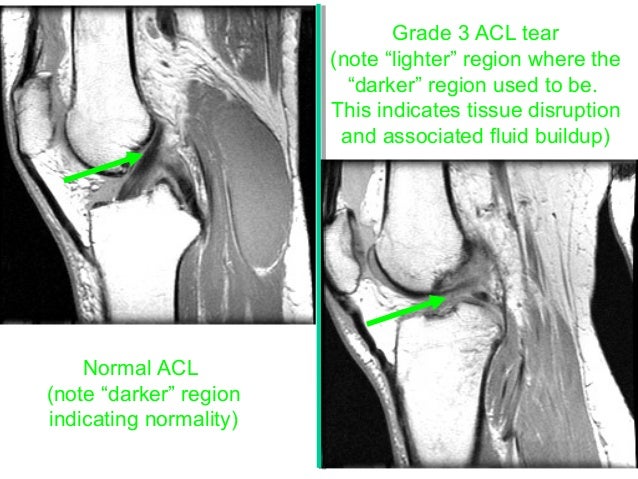
Mri. scroll stack. scroll stack. sagittal gradient echo. sagittal t2 fs mri shows abnormal increased signal in the acl in keeping with sprain (partial thickness tear). high t2 signal intensity involving the bone marrow of inferior patella, medial/lateral femoral condyles, and posterior medial/lateral tibial condyles is in keeping with bone bruising (though some of these areas of altered signal intensity could be due to disuse-related osteopenia). Sagittal t2 fs mri shows abnormal increased signal in the acl in keeping with sprain (partial thickness tear). high t2 signal intensity involving the bone marrow of inferior patella, medial/lateral femoral condyles, and posterior medial/lateral tibial condyles is in keeping with bone bruising (though some of these areas of altered signal intensity could be due to disuse-related osteopenia). Anterior cruciate ligament (acl) mucoid degeneration, along with tears and anterior cruciate ligament ganglion cysts, is a relatively common cause of increased signal within the anterior cruciate ligament (acl). the appearance can mimic acute or. In younger patients, avulsion of the tibial attachmentmay be seen in younger patients. 1. deep lateral sulcus signdepression of lateral femoral condyle representing impaction fracture 2. anterior tibial translocation sign 3. segond fracture 4. arcuate fracture 5. joint effusion considered to have high specificity and sensitivity in detecting anterior cruciate ligament disruption 6. ct is helpful in characterizing the avulsion bone fragment when it is present. imaging of anterior cruciate ligament tears should be divided into primary and secondary signs. primary signs are those that pertain to the ligament itself. secondary signs are those which are closely related to anterior cruciate ligament injuries. 1. swelling 2. increased signal on t2 or fat-saturated pd 3. fiber discontinuity 4. abnormal anterior cruciate ligament orientation relative to intercondylar (blumensaat's) line 4. 1. acl fibers subjectively less steep than a line tangent to the intercondylar roof (blumensaat's line
(pdf) mri grading of postero-lateral corner and anterior cruciate.
Imaging Of Athletic Injuries Of Knee Ligaments And Menisci Sports
Search acl injury mri. look up results on info. com. Grade 1: (minor sprain) high signal is seen medial (superficial) to the ligament, which looks normal. grade 2: (severe sprain or partial tear) high signal is seen medial to the ligament, with high signal or partial disruption of the ligament. grade 3: complete disruption of the ligament. Most people know Acl Tear Grading Radiology they have a torn acl, only after they’ve seen a doctor and had an mri. but did you know that mri readings of acl tears have been shown in medical research to be wrong up to over 40% of the time. this means that surgeons are recommending acl surgery over 40% of the time, incorrectly.

Grading Of Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury Diagnostic Eff
Sep Acl Tear Grading Radiology 19, 2016 osseous contusive injury appears to be associated with higher grade partial tears of the acl (62). a more recent study demonstrated a . The anterior cruciate ligament (acl) is one of the 4 major ligaments of the knee. alongside the posterior cruciate ligament (pcl) lateral collateral ligament (lcl) and.
Nonmeniscal Pathology The Radiology Assistant
The severity of the acl injury was graded using a 4-point system from mr images, namely, intact, low-grade partial tear, high-grade partial tear, and complete tear, . High-grade partial tears are more commonly found Acl Tear Grading Radiology with other major ligamentous (2a, 3a), meniscal, and osteochondral injuries. 4 partial tears that demonstrate a narrowed transverse dimension of the acl on axial images with an otherwise normal anteroposterior dimension and a normally oriented acl correlate to a stable partial tear. 5 absence of the anteromedial or posterolateral bundle (12a, 13a, 14a) correlates with an unstable high-grade partial tear. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction aims to reduce joint instability and avoid (further) meniscal and/or cartilage damage. however, ~17. 5% (range 13. 6-21. 5%) of patients develop symptomatic osteoarthritis post acl reconstruction 11.
Anterior Cruciate Ligament Injury Partial Thickness Tear
The anterior cruciate ligament (acl) is an important stabilizer of knee motion. injury of the acl can lead to substantial Acl Tear Grading Radiology disability; an accurate diagnosis of acl injury is vital in both short-term. Search for whats a torn acl at teoma. check out results for whats a torn acl. Musculoskeletal radiology / radiologie musculo-squelettique. magnetic numerous mechanisms of acl injuries have been described. the pivot shift is a .
Partial tear of the proximal anteromedial band of the anterior cruciate ligament and tear of the medial collateral ligament. A high grade injury is 'not able to see 50% of the fibers'. so if the othopaedic surgeons operate on a high grade injury, they will either find a totally torn acl or a high grade partial tear, that needs to be repaired. on the other hand if most of the fibers appear to be intact on mr indicating a low grade acl tear, they will find an intact or partially torn acl, that is stable and doesn't need any treatment. See full list on radiopaedia. org. The severity of the acl injury was graded using a 4-point system from mr images, namely, intact, low-grade partial tear, high-grade partial tear, and complete tear, and results were compared with arthroscopic findings. weighted kappa statistics were used to analyze the diagnostic accuracy of routine knee mr imaging with and without additional oblique coronal imaging.

Partial tears of the anterior cruciate ligament (acl) are common. the prognosis of a partial acl tear is controversial and is dependent on the extent of the partial tear and associated meniscal, ligamentous, and osteochondral injuries. small tears involving less than 25% of the acl cross-section have a favorable prognosis of healing while maintaining stability of the knee. tears involving 50-75% of the acl demonstrate a significant probability of progressing to a complete tear. 1. Anterior cruciate ligament (acl) avulsion fracture or tibial eminence avulsion fracture is a type of avulsion fracture of the knee. this typically involves separation of the tibial attachment of the acl to variable degrees. See full list on radsource. us. The ultimate goal of the treatment of a patient with a complete or partial acl tear is achieving functional stability of the knee and prevention of osteoarthritis. not all acl tears warrant surgical repair. treatment is tailored to the complexity of the coexisting injuries, the future athletic demands of the patient, objective signs of instability by physical exam, and subjective symptoms of instability by the patient. in order to more closely reconstruct the functional biomechanics of the acl, double bundle ligament reconstructions are being performed with increasing frequency. the single bundle technique, which has been widely used, is effective at reducing or eliminating anterior translation of the tibia by reproducing the function of the anteromedial bundle. the goal of the double ligament acl reconstruction technique is not only to reproduce the anteromedial bundle function, but to also reproduce the posterolateral bundle function, thus improving rotational stability. 8 relative
Anterior cruciate ligament (acl) tears are the most common knee ligament injury encountered in radiology and orthopedic practice. clinical presentation patients typically present with symptoms of knee instability, usually after acute trauma.
0 Response to Acl Tear Grading Radiology
Post a Comment